As从句归纳总结
一、As引导定语的特点
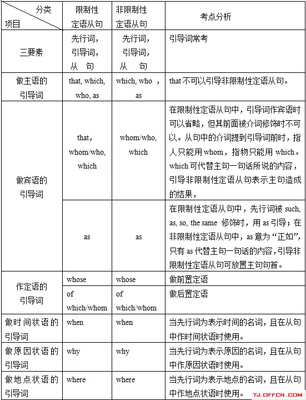
在定语从句中,一般的从句关系代词是which、who、whom、that、whose,其代替主句中的人或物,在从句中做主语、宾语或定语。而学生在学习过程中,常会遇到as作为关系代词出现,学生对as定语从句多有疑惑,现对as作为关系代词引导定语从句的情况做一归纳,以供参考.
一)as引导限制性定语从句
主要结构有:
thesame…asas…assuch…asso…as主句中出现the same, as,such, so修饰先行词,需选择as做关系代词在定语从句中做主语或宾语。
1. It’s the same person as we wanted to find yesterday.我们昨天要找的是同一个人。
2. Such girls as he knows are good at English.他所认识的女孩都擅长英语。
3. Do you have such books as we like ?你有我们喜欢那种书吗?
4. She will marry as healthy a man as she can find.她将嫁给她能找到的任何一个有钱人。
5. There is so warm a house as we want to live in.这里有如此暖和的房子,我们都想住在里面。
6. He has so difficult a problem , as none of us can solve.他有如此难的一个问题,我们没有人能解决。
二、引导非限制性定语从句
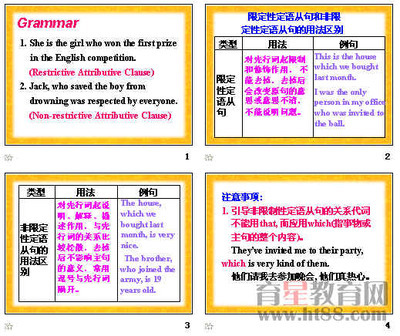
1. as引导非限制性定语从句,指代整个主句内容,从句可置于句首,句中或句尾
1) As everyone knows ,China is a beautiful country with a long history.每个人都知道,中国是一个有着悠久历史的美丽国家。
2) The earth , as we know , moves round the sun.地球,我们都知道,围着太阳转。
3) Tom works hard and is willing to help others, as we allknow.汤母工作努力,并且乐于助人,这一点我们都知道。
2. 非限制性定语从句中的谓语为被动式时,常用as做主语
besaid/known/announced/reported
bementioned/expected/discussed
1) Grammar , as hasbeen said before, is not a set of deadrules.语法,就像以前所说,不是一套死规则。
2) As is known toall, Taiwan is part of China .
3)As isillustrated in the picture,one drop of water does not make asea;one tree does not make a forest;one person does not make asociety.
3. as引导非限制性定语从句,有“如,似,正像”的含义,因此,下列句式多用as
1) as has been saidabove 如上所说
2) as anybody cansee正像每个人所看到的那样
3) as we hadexpected正如我们所预料的那样
4) Things are notalways as they appear.事情并不一直像他们表面那样。
5) The boy has asmuch progress as we hadexpected.正像我们所预料的那样,这个男孩取得了大的进步。
二) As引导的定语从句与which引导的定语从句的区别
(一)在限制性定语从句中的区别:
1.as 的用法:其通常和such the same连用,代指物在从句中做主语或宾语
1) This is the same pen as I boughtyesterday。这种笔和我昨天买的笔一样(同样的但不是同一个)。
引导定语从句的关系词在从句中做宾语,因先行词被the same所修饰所以用as引导
注意:上句与下句的区别
2) This is the same pen that I usedyesterday.这就是昨天我使用的那一支钢笔(指的是同一个)。
3) I want to have such a dictionary as he has.我想要一本和他的一样的字典。
2. 引导定语从句的关系词在从句中做宾语,因先行词被such所修饰所以用as引导
which的用法:关系代词,在从句中做主语或宾语,做宾语时通常可以省略(直接做介词的宾语时除外,不能省。)
1) The radio whichhe bought yesterday doesn't work now.他昨天买的收音机现在坏了。引导定语从句的关系代词在从句中做宾语,代指物,故用which.
2) Can you lend methe book which was written by Lun Xun.你能借我那本由鲁迅所写的书吗?
引导定语从句的关系代词在从句中做主语,代指物,故用which.
3) This is the parkwhich is the most beautiful one in our city.这是我们这个城市最漂亮的公园。引导定语从句的关系代词在从句中做主语,代指物,故用which.
4) This is the mapby which we can get to the forest.这是张地图,借助它我们能到达那个森林。引导定语从句的关系代词在从句中做介词的宾语,代指物,故用which.
二)在非限制性定语从句中的区别:
1. as的用法:
①在从句中通常做主语代指整个主句,
②表示的意思是正如、正象
③其引导的定语从句即可以放在主句之前也可以放在主句之后。
1) The Pacific isthe largest ocean, as we all know.太平洋是最大的洋,这一点我们都知道(正如我们所知到的,太平洋是最大的洋)。
引导非限制性定语从句的as在从句中做know的宾语,其代指整个主句。
2) As we expect, wewon the game. 我们赢了,这一点在我们预料之中。(正如我们预料的一样,我们赢了)。
引导非限制性定语从句的as在从句中做主语,其代指整个主句。as引导的定语从句即可以放在主句之前。
3) The earth isround, as we all know.地球是圆的,这一点我们都知道。(正如我们所知到的一样地球是圆的)引导非限制性定语从句的as在从句中做know的宾语,其代指整个主句。
4) As is known toall, he is the best student in our class. 众所周知,他是我们班上最好的学生。(正如我们所知到的一样,他是我们班上最好的学生。
引导非限制性定语从句的as在从句中做主语,其代指整个主句。as引导的定语从句即可以放在主句之前。
2. which的用法:
①关系代词,在从句中做主语或宾语,代指物。
②当代指整个主句时表示的意思是主句和从句之间是因果关系即因为所以。
③其引导的非限制性定语从句只能放在主句之后。
1) Tom suddenlyfell ill, which made us sad.Tom突然病倒,这使得我们很伤心。Which引导的非限制性定语从句在从句中做主语,其代指整个主句,主从句的关系是因果关系,因为他的病,所以我们伤心。
2) The road was tooslippery, which caused lots of accidents.路太滑了,以至于引起了很多事故。Which引导的非限制性定语从句在从句中做主语,其代指整个主句,主从句的关系是因果关系,因为路滑,所以出事。
3) He was angry,which made himcry.他太生气了以至于他哭了起来。Which引导的非限制性定语从句在从句中做主语,其代指整个主句,主从句的关系是因果关系,因为生气,所以哭。
二. as引导的状语从句
1、as表示“因为”、“由于”,引导原因状语从句,其语气不如because强,通常为附加说明的理由,且是已知晓的原因,主句与从句没有逻辑上的因果关系。例如:
As she was notwell, I went there alone. 因为她身体不好,所以我独自到那里去了。
As he is atailor, he knows what to do with this material.由于他是个裁缝,他知道怎样利用这块布料。
as=since, 作既然、由于解,引导原因状语从句,常用来表示已为人们所知或显而易见的原因或理由。如:
As / Since you're not feeling well, you may stay at home.
As he wasn't ready in time, we went withouthim.
2.as表示“虽然……但是……”,引导让步状语从句,从句通常用倒装语序,把从句的表语、状语或动词原形放在as前面,可以用though替代。例如:
Child as he is,he knows a lot. 虽然他是个孩子,但他知道的东西很多。
Hard as it wasraining, they went on working in the field.虽然天下大雨,但他们继续在田地里干活。
3.as表示“按照”、“依照”、“像”,引导方式状语从句,从句置于主句之后。例如:
You should do asthe teacher tells you.你应当依照老师所说的去做。
The absence ofair also explains why the stars do not seem to twinkle in space asthey do from the earth.空气的不存在,也说明了为什么在空中星星看来并不闪烁,而不像从地球上看的那样。
as=in the way that, 作像、按照……的方式解,引导方式状语从句。如:
He speaks English as Americans do.
Remember, you must do everything as I do.
4.as表示“像……一样”,引导比较状语从句,对主句和从句的动作或状态加以比较,说明它们之间有相似之处,在从句中常省略与主句相同的部分。例如:
He doesn't workas hard as I (do). 他不像我工作那样努力。
I hope thenecklace was as good as the one you lentme.我希望我挂项链同你借给我的一样好。
用于as...as...或not so/as...as...中,前一个as是副词,后一个as是连词,引导比较状语从句。如:
They helped the old man as often as possible.
I don't speak English so/ as well as he does.
5.as表示“当……的时候”,引导时间状语从句,多强调主句和从句中的动作或状态同时发生,从句可放在主句前,也可放在主句后。例如:
As I waited atthe stop, I heard a big noise.当我在车站等车的时候,我听到一个很大的声响。
She rose up ashe entered. 当他进来时,她站了起来。
as作从属连词用时,可以引导五种状语从句。现归纳如下:
as引导时间状语从句表示“当……的时候”“在……期间”时,该从句的谓语通常是那些表示动作意义的动词,而不能是be(是、在),have(有),like(喜欢),belong(属于)等表示状态或静态意义的动词。
我打算去邮局。——当你在邮局的时候,请帮我买几张邮票好吗?
误:I’m going to thepost office.—As you are there, can you get me somestamps?
正:I’m going to thepost office.—While you are there, can you get me somestamps?
1.作当……的时候,引导时间状语从句。注意与when、 while的用法区别。
① when作当……的时候解,可以指较短的(一点)时间,也可指一段时间。如:
When he was at college, he could speak several foreignlanguages.
When the clock struck twelve, all the lights in the street wentout.
② while常表示一段较长的时间或一个过程,强调主句谓语动词与从句谓语动词同时发生。如:
Work while you work. Play while you play.
■正因为 as引导时间状语从句表示“当……的时候”“在……期间”时,从句的谓语不能是表示状态或静态意义的动词,所以当下面第一句变为第二句这样的状语从句时,不能再用as,而应用 when:
As a student he had knowngreat poverty.
但属下列情形时,只用as,而不用when或while。
A) 用于表示同一个人的两种动作交替进行,指一边……,一边……。如:
The girl dances as she sings on the stage.
He looked behind from time to time as he went forward.
B)表示两个同步发展的动作或行为,译为随着……。如:
As time went on / by, she became more and more worried.
As children get older, they become more and more interested in thethings around them.
C)表示两个短促行为或事件几乎同时发生。如:
I thought of it just as you opened your mouth.
Just as the flying worm hit her face, she gave a loud cry.
D) 后接名词表示某一年龄段时,用as。如:
As a young man, he was active in sports.
 爱华网
爱华网